2. σ- and π-Organo Complexes of Rh and Pt
Rhodium and platinum are top candidates for the formation of stable ó- and ð-organo complexes. Furthermore, organorhodium and -platinum complexes are involved in homogeneously catalyzed processes. Thus, organometallics of these elements are suitable to study the interplay between stabilization and activation of organo ligands. Some results of our investigations in this field are:
- Synthesis and characterization of dinuclear oligo-methylene-bridged organorhodoximes [Rh]-(CH2)n-[Rh] (n = 2 - 5; [Rh] = Rh(dmgH)2(PPh3); dmgH2 = dimethylglyoxime) as well as of novel cyclic and reduced organorhodoximes, see Fig. 4 and 5 as example. 2-functionalized ethyl complexes [Rh]-CH2-CH2-YRn have been shown to undergo heterolytic fragmentation reactions.
- Hexachloroplatinic acid catalyzes the addition of n-butanol to alkynes to give acetals or ketals. With internal alkynes, RCCR cyclobutadiene platinum complexes [PtCl2(C4R2R`2)] and [PtCl2(C4R2R`2)L] (L = neutral N-, P-, As-donor) are formed. With silyl-substituted alkynes dinuclear platina-â-diketones [Pt2{(COR)2H}2(µ-Cl)2] are formed (see Fig. 6). These complexes exhibit a unique reactivity because they are electronically unsaturated complexes with a kinetically labile ligand sphere.
- Platina-â-diketones react with bases to give platina-â-diketonates of platina-â-diketones that can be regarded as organometallic analogues of platinum blue complexes (see Fig. 7). With phosphorus donors complexes they react like "hydroxycarbene/acyl" complexes under cleavage of aldehydes. With chelating N-donors (like bpy), they react to give acyl(hydrido)platinum(IV) complexes (see Fig. 8) that exhibit an astonishing thermal stability (Tdec > 150 °C!)
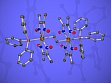
Figure 4: Structure of (PPh3)(dmgH)2Rh-CH2-CH2-Rh(dmgH)2(PPh3), a binuclear organorhodoxime.
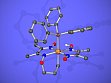
Figure 5: Structure of an organorhodoxime with a six-membered 1-aza-2-oxa-3-rhodacycle.
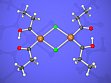
Figure 6: Molecular structure of a platina-β-diketone: [Pt2{(COEt)2H}2(µ-Cl)2].
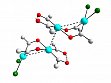
Figure 7: [{Cl2Pt(µ-COMe)2Pt[(COMe)2H)]}2], an organometallic analogue of a platinum blue complex exhibiting the typical Pt4 zig-zag-chain.
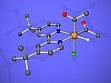
Figure 8: Molecular structure of [Pt(COMe)2(H)Cl{4,4´-(t-Bu)bpy}], an acyl(hydrido)platinum(IV) complex.



