Kontakt
Verantwortlich:
Prof. Dr. Carsten Tschierske
Telefon: 0345 5525664
Telefax: 0345 5527346
carsten.tschierske@chemie.u...
Raum 102
Kurt-Mothes-Straße 2
06120 Halle
Postanschrift:
Martin-Luther-Universität Halle-Wittenberg
Naturwissenschaftliche Fakultät II
Institut für Chemie
Organische Chemie
Kurt-Mothes-Straße 2
06120 Halle (Saale)
GERMANY
Polyphilic molecules with membrane modifying properties
The aim of this project is the synthesis of new polyphilic molecules, among them facial amphiphiles and bolaamphiphiles with T- or X-shaped structure and composed of three or four incompatible segments, which represent rigid units, polar groups capable of hydrogen bonding, lipophilic chains and fluorophilic segments (see Figures 1 and 2). A first target is the development of synthetic pathways to polyphilic molecules with extended hydrophilic units, good solubility in water and capability to self assembly in aqueous systems. Moreover, the structure of the lipophilic and rigid units is adjusted to the dimensions of lipid membranes and systematic structural variations are carried out in order to study the effects of the changes of the molecular structure on the self assembly in lyotropic LC phases, Langmuir films and durig the interaction with model lipid membranes.
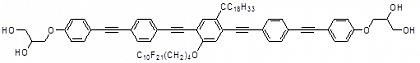
Figure 1: Example for an X-shaped polyphile capable of spanning the membrane and modifying the structure and stability of GUVs; for formation of complex LC phases with related molecules, see: X. Zeng Et al. Science, 2012, 331, 1202.
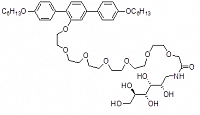
Figure 2: Example of a polyphile, used for forming hexagonal bicelles with phospholipides (see Scholtysek et al., J. Phys. Chem. accepted)
The synthesized molecules are investigated under different aspects with different methods:
- Self assembly behaviour in thermotropic and lyotropic LC phases is studied by means of polarizing microscopy, DSC and XRD methods.
- The aggregation in diluted aqueous solutions is studied by DSC, electron microscopy and other methods (TP 4 Blume).
- Formation of thin ordered films at the air water interface are investigated with a Langmuir film balance, Brewster angle microscopy, (TP 3 Kressler) IRRRAS (TP 4 Blume) and additional techniques, and the films are transferred to solid substrates which are investigated by AFM and XRR (TP 3 Kressler; University Warsaw: Holyst).
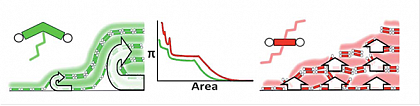
Figure 3: Formation of well defined multilayers at the air water interface which are modified by the chemical structure of the polyphile. (Paczesny, J. et al., Soft Matter, published on-line, DOI: DOI: 10.1039/c2sm00022a.)
- The interaction with lipid membrane models, such as vesicles and giant unilamellar vesicles (GUVs) is investigated with several partners (TP 4 Blume, HALOMEM Bacia). The effects on the membrane dynamics are investigated in TP 5 (Saalwächter) by NMR methods.
The goal is to explore the effects of synthetic polyphilic molecules on membrane structure and membrane properties and to understand the relations between specific features of the molecular structure and the effects on model membranes.



